Knowledge of the Difference between Conductor and Insulator is basic physics and general electrical practice. In domestic wiring and some of the most sophisticated electronic equipment, the materials used are selected according to their ability or inability to conduct electric current. When subjected to electricity, heat, or energy transfer, a conductor and an insulator act in contrast. Although conductors facilitate the free flow of electrons, the insulators resist the flow and protect and regulate it. The current article describes thedistinction between conductor and insulator, their characteristics, examples, and practical applications, so that the students and readers can clearly understand why both are vital in contemporary life.
What Is a Conductor?
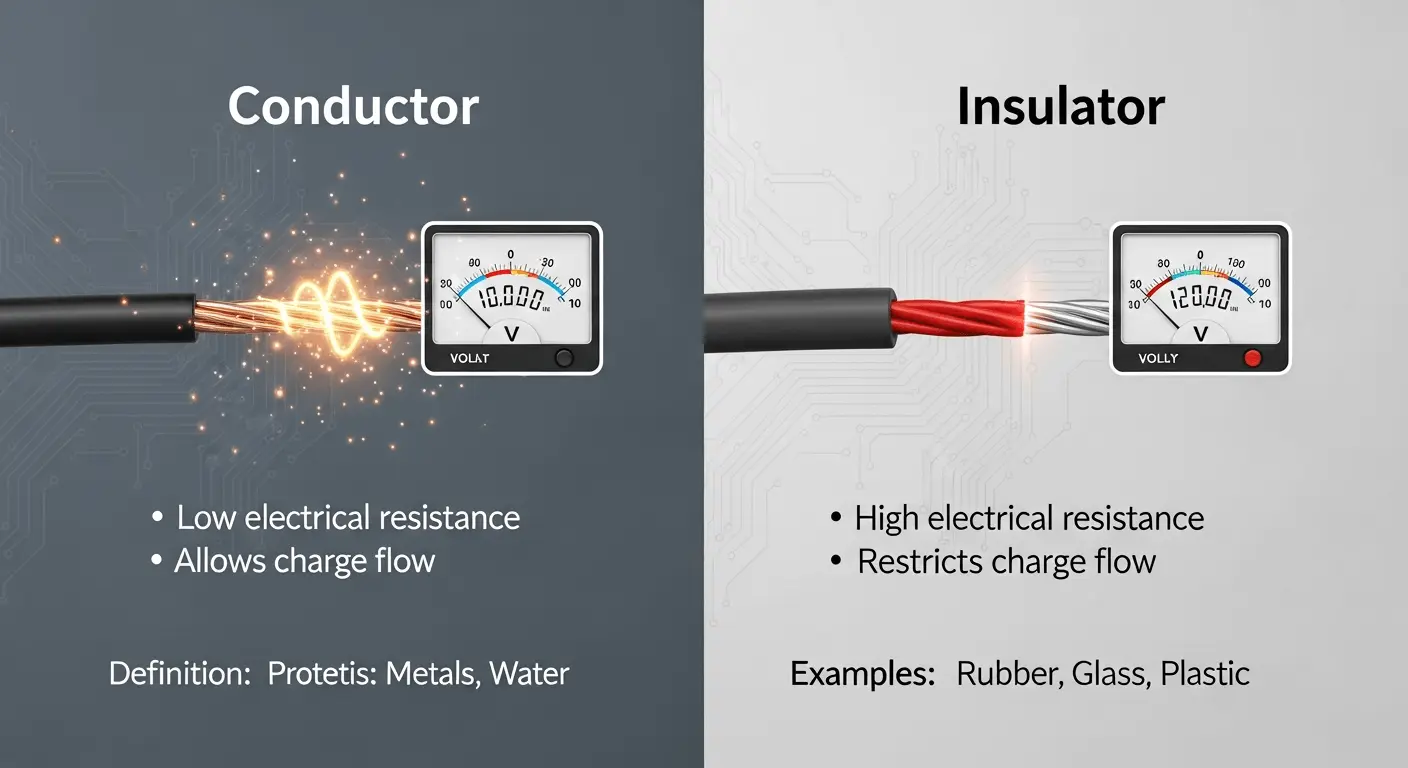
A conductor is a substance that is easily penetrated by an electric current or heat. Conductors are the ones that contain free electrons that flow with the application of voltage. This characteristic of free movement of the electrons renders conductors very effective in the transmission of electricity.
Typical examples of conductors are copper, aluminum, silver, gold, and iron. Copper is also popular in electrical wiring due to its low resistance, conductivity, and durability at a comparatively low cost. The atomic structure of metals usually facilitates electron movement, making them good conductors.
Materials such as metals are also heat conductors in terms of thermal energy, and this is the reason why cookware is usually crafted out of aluminum or steel. In the case of the study of the distinction between conductor and insulator, conductors are always related to a low resistance and high energy transfer efficiency.
What Is an Insulator?
An insulator refers to a substance that facilitates neither the movement of electric current nor heat. Insulators are tightly bound electrons within a conductor and insulator structure, making it hard to conduct electricity. Such resistance is important for safety and energy control.
Insulators are examples of rubber, plastic, glass, wood, air, and ceramic. They are usually used in coating electrical wires, and this helps to avoid accidental shocks and short circuits. In the absence of insulators, electrical systems would be very unsafe.
In the inspection of the distinction between conductor and insulator, there is the protective role of insulators. They do not conduct electricity but tend to block or restrict the flow of the current to make sure that the current flows in the way it is supposed to.
Major Difference between Conductor and Insulator
The major distinction between a conductor and an insulator is that they can conduct energy. Conductors permit the passage of electricity and heat freely, whereas insulators permit the passage or total prohibition of electricity and heat. Low electrical resistance conductors’ insulation. High electrical resistance insulators.
The other distinction of significance is their use. Transmission is done using conductors like wires, cables, and circuits, and protection and isolation are done using insulators. The conductor and an insulator are together, yet they create the basis of safe and efficient systems in electricity.
Why the Two Are Significant in Everyday Life
The insulator and the conductor are in a complementary relationship. Electrical devices are operated by conductors and insulated to prevent injuries to the users. From mobile chargers to power grids, the equal use of the two materials guarantees performance, safety, and reliability.
The knowledge of the difference between a conductor and an insulator assists the students, technicians, and consumers in making well-informed decisions and better appreciating the fact that electricity is used to power the modern world. Click here to see more details.



